Basic usage¶
fancplot is modular and multiple plots can be combined into a single figure.
Each plot can be configured individually, with a number of customisation options.
There are two modes: by default, an interactive plot opens in a new window, which allows synchronised scrolling, zooming and panning for plots that support it. By specifying an output file, the plot is saved to file directly.
Overview¶
fancplot plotting tool for fanc
usage: fancplot [<fancplot global parameters>] <region> [<region> ...]
--plot <plot type> [<plot parameters>] <plot data file(s)> [...]
Run fancplot --plot <plot type> -h for help on a specific subplot.
Plot types:
-- Matrix --
triangular Triangular Hi-C plot
square Square Hi-C plot
split Matrix vs matrix plot
mirror "Mirrored" matrix comparison plot
-- Region --
scores Region scores plot with parameter dependency
line Line plot
bar Bar plot for region scores
layer Layered feature plot
gene Gene plot
Positional Arguments¶
- regions
List of region selectors (<chr>:<start>-<end>) or files with region information (BED, GTF, …).
Named Arguments¶
- -o, --output
Suppresses interactive plotting window and redirects plot to file. Specify path to file when plotting a single region, and path to a folder for plotting multiple regions.
- -s, --script
Use a script file to define plot.
- -p, --plot
New plot, type will be chosen automatically by file type, unless “-t” is provided.
- -n, --name
Plot name to be used as prefix when plotting multiple regions. Is ignored for single region and interactive plot.
- --width
Width of the figure in inches. Default: 4
- -w, --window-size
Plotting region size in base pairs. If provided, the actual size of the given region is ignored and instead a region <chromosome>:<region center - window size/2> - <region center + window size/2> will be plotted.
- --invert-x
Invert x-axis for this plot
- --tick-locations
Manually define the locations of the tick labels on the genome axis.
- -V, --version
Print version information
Setting up the figure and plotting regions¶
The main argument of fancplot is a region specification. You can list one or more
regions by region selector (of the form <chromosome>:<start>-<end>), or you can
provide the path to a file with region information (BED, GFF, FAN-C
object, …). You can also mix the two. Regions will be plotted in the order they are
listed with the next plot appearing after the previous one has been closed.
# single region
fancplot chr18:6mb-10mb
# multiple regions
fancplot chr18:12000000-14000000 chr18:6.5mb-10mb
# BED file
fancplot /path/to/file.bed
By default, fancplot plots exactly the area that is provided. It is, however,
also possible to merely center the plot on the provided region, and to set a fixed
plotting window using the -w option. This is especially useful when providing
regions from other analyses, such as ChIP-seq peaks or insulation boundaries,
and allows you to quickly survey other genomic features in their immediate surrounding.
fancplot -w 1mb /path/to/chipseq.narrowPeak
By default, fancplot will open an interactive plotting window. With the -o <path>
argument, it is possible to directly plot to a file. The file ending determines its
type.
fancplot -o /path/to/plot.png chr18:6mb-10mb
When specifying multiple regions, the output argument will be interpreted as a folder,
and each plot will be named by the pattern
<region index>_[<prefix>_]_<chromosome>_<start>_<end>. The <prefix> can be added
using the --name argument.
The figure width is controlled using the --width argument (4 inches by default).
The figure height is determined automatically from the figure width, the number of
panels, and their aspect ratio.
Adding panels¶
After setting up the figure and plotting region(s), you can start adding plots to the
figure. On the command line, the -p or --plot argument adds a new panel. You need
to provide the type of plot you want immediately after -p:
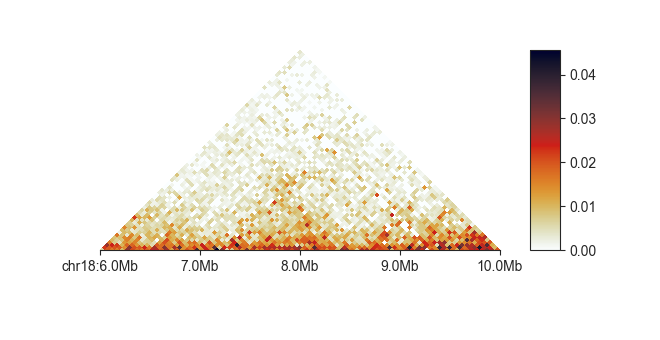
fancplot chr18:6mb-10mb -p triangular
A basic call to fancplot, plotting a 4 Megabase region on chromosome 18 of a Hi-C matrix
in a triangular heatmap, could look like this:
fancplot chr18:6mb-10mb -p triangular output/hic/binned/fanc_example_50kb.hic
fancplot tries to find a sensible placement of ticks and ticklabels on the genome axis,
but if you prefer different tick locations or if labels are overlapping in small figures,
define your own custom labels with the --tick-locations argument.
fancplot chr18:6mb-10mb --tick-locations 8mb 10mb -p triangular output/hic/binned/fanc_example_50kb.hic
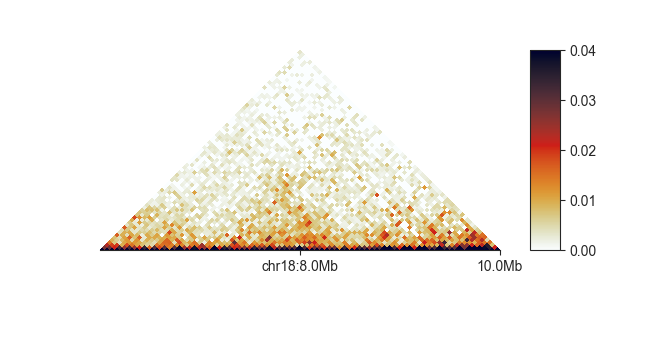
The first label will always get a chromosome prefix.
To get help on a specific panel type, and list available parameters, use -h after
the plot type:
fancplot chr18:6mb-10mb -p triangular -h
Common parameters¶
A few parameters are supported by all panel types. For example, you can set a title above
a panel using the --title parameter.
You can format the genome axis in various ways. For example, add minor ticks between the
major ones on the genome axis using --show-minor-ticks, or hide the major
ticks, too using --hide-major-ticks. You can add a small legend to the panel showing
the distances between minor and major ticks, as well as the size of the plotting region
with --show-tick-legend. You can hide the x axis altogether with --hide-x.
The aspect ratio of each plot controls the height of the y axis relative to the width
of the x axis. For example, the default aspect ratio of the square plot is 1.0
while the default for triangular is automatically determined so that the matrix is
not distorted.
Sometimes there might be a nomenclature mismatch in the data backing different panels
regarding chromosome naming (with or without the chr prefix). Rather than having to
reformat your data to match with the plotting region definition, you can correct for
this issue on the fly, for each panel separately using --fix-chromosome.
In the following sections we will introduce the different Panel types in more detail.